AI Implementation Guide
Introduction
This guide is intended for professionals involved in designing and managing business processes within WEBCON BPS.
The goal is to provide practical instructions and best practices for implementing AI functionalities (AI Agent, AI PROMPT, AI Concierge) into new or existing workflows.
Overview of AI Functionalities
AI Agent
An autonomous agent is assigned to execute a Job on a particular step of a workflow. For every element entering this step, a new Job will be added to Jobs Queue. Jobs are then processed by Webcon Workflow Service. The result will depend on given instructions. Usually it's filling form fields and selecting a path to a next step.
AI Agent can be added on any starting, intermediate, system or final step by clicking an AI icon in the bottom left corner of the step. If an AI Agent is already added, this icon will be coloured.

When executing a Job, AI Agent:
- respects all settings from the form field matrix. Only editable fields can be changed, only visible fields will be added to context.
- this includes technical fields.
- it is not guaranteed, that AI will provide values for all required fields (if not sure, it will leave the field empty). For that reason, it's best to leave fields as optional, or disable form fields validation on paths used by AI Agents.
- has access to metadata, such as process, workflow, step, task and form fields descriptions.
- can read attachments related to the given instructions (AI Agent will decide, which one to read based on instructions and files names).
AI PROMPT
Is a business rule, that sends a single PROMPT to LLM and returns its response. It can be used as any other business rule in the system. This gives it a lot of flexibility, but requires more configuration and setup to incorporate it with other actions and business rules to create sophisticated automatons.
AI PROMPT takes two arguments:
- task (required) - text based instructions or a list of attachments.
- system instruction (optional)
and returns text.
See structured output to learn, how to deal with AI PROMPT responses.
AI Concierge
Is a personal assistant to a user. Based on instructions and attached files, AI Concierge can:
- fill the form,
- only editable fields can be modified
- it is not guaranteed, that AI will provide values for all required fields (if not sure, it will leave the field empty).
- suggest a transition path,
- suggest a menu action button,
- describe the form,
AI Concierge doesn’t make permanent changes to the form. Instead, it suggests possible actions. It’s up to the user to review and confirm these actions. This ensures control stays with the user, while the AI Concierge provides guidance.
The more clearly a form is structured - with meaningful field names, helpful descriptions, and well-defined tasks details - the better AI Concierge can understand the context and assist the end user in completing the task.
Vague labels or jargon can confuse the AI Concierge and lead to unexpected results.
Most of this article is aimed towards AI Agent and AI PROMPT. AI Concierge just works out of the box, without any configuration. However, to write better instructions and use it more efficiently, check internal tools to better understand it's capabilities.
Comparison
| Feature | AI Agent | AI PROMPT | AI Concierge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Step | Business rule | Chat assistant |
| Configuration required | Yes | Yes | No |
| Triggered by | Entering a workflow step | Depends on configuration | User interaction |
| Access to attachments | Yes (auto-selected) | Yes (as input parameters) | Yes (added to chat) |
| Ability to modify elements | Yes | No (returns text only) | No (suggestions only) |
| Response format | Structured | Plain text | Structured / Suggestions |
All AI Functionalities support a limited number of file types: "txt", "pdf", "xml", "rtf", "csv", "html", "md", "jpg", "png", "webp", "docx", "doc", "bpmn", "msg", "tif", "bmp", "svg"
Pilot Implementation
All AI functionalities can be implemented directly into existing processes, automating that, which was not previously possible. To minimize disruption and still be able to test new functions in production environment, it's beneficial to deploy AI within a controlled and limited scope.
AI PROMPT can be created as a menu action, invoked on demand by end users and immediately verifying the output. Once ready, these actions can be incorporated into existing automation.
Additional flow control step can redirect a subset of the workflow elements to AI Agent, and the rest to a usual flow.
Identifying Candidate Workflows
- Criteria for selection
- Repetitive tasks
- Decision points requiring non-deterministic decision making
- Prioritization factors
- High-volume processes
- Known bottlenecks
Use cases and examples
AI Agents
Pre-processing Tasks
- Information summarization
- Suggested inputs based on historical data
Example: Content review - AI Agent can review an article before it goes to final approval. During pilot phase, only selected content can be sent to be reviewed by AI and the rest of the process can remain unchanged.

Context-Based Flow Control
- Path selection based on non-deterministic inputs
Example: Mail classification - had to be manual task, now can be supported by an AI Agent

AI PROMPT
AI PROMPT can often be a good starting point to evaluate, if AI can make a difference in a given area.
Using the "Content Review" workflow as an example: In the first version, review can be generated by AI PROMPT instead of AI Agent, this allows it to be used as menu action, invoked on demand by the reviewer. Once a certain level of accuracy is reached, AI Agent can take over the task of reviewing content.
Prefer AI PROMPT over AI Agents, when end user needs to get immediate response from AI.
AI Concierge
Contrary to AI PROMPT and AI Agents, AI Concierge does not require any configuration. Thus use cases will most likely be discovered by end users, not imposed by the administrators. Make sure to gather feedback and share knowledge among users.
Example message templates for AI Concierge:
- Fill the form (if attachments are added to context, form will be filled based content)
- Set (field name). (tasks description - change tone - summarize - format to HTML (for multiple lines fields with rich editor) - translate to (language))
Use voice typing with native device capabilities (on Windows it's [Windows key] + H).
Instruction Design
Simple prompts
Try using simple prompts first. Run them on few examples to see the result. Based on that, create next versions of instructions by adding and testing small changes.
// AI Agent
Based on the attachment, choose the appropriate transition path.
// AI PROMPT, system instruction
Prepare content according to the given topic and specified style.

Use simple ROLE > TASK template
// AI Agent or AI PROMPT
# ROLE
You are a creative content creator specializing in marketing materials designed for use across various communication channels.
You are familiar with the latest trends in the low-code platform market, and the content you create relates to topics such as business process automation, low-code, RPA, etc.
# TASK
Prepare content according to the given topic and specified style.
For longer prompts, it is advisable to use alternative business rules to improve readability and maintainability. One example, using COLLECTION, was presented earlier. Another useful option is the TEXT rule, which supports multiline editing and facilitates working with more complex instructions.


More prompt templates can be found in various tutorials online and can be used just as well.
Focus on one tasks
Instructions should be focused on one task. When an operation requires multiple steps, it is worth splitting it into several AI PROMPTs or AI Agents.
AI PROMPT can be chained by passing the result of one rule to another by form fields, local automation parameters or nesting them directly. This works well with structured outputs.
AI Agents can be chained by creating several subsequent workflow steps.
Two examples of such approach:
- gathering info about a company and generating summary of recent developments
- writing and reviewing content

Use existing descriptions
AI Agent and AI Concierge have access to more than just instructions given by in their configuration. They also know about the tooltips for each form field and path as well as step description. Relying on descriptions and tooltips is especially useful when introducing AI Agents into existing workflows.
Consider an example workflow, in which incoming mail is categorized by an AI Agent (workflow diagram is presented above). Simple instructions (like one mentioned before "Based on the attachment, choose the appropriate transition path.") may be enough, but providing clear classification hints will allow AI to make better decisions in less obvious cases.
One solution, is to put hints directly into AI Agent instructions.

Just as well, these hints can be added as path description.

The AI Agent also knows about step descriptions, so the final configuration may have some task described in step description and the instruction is simply to ask AI Agent to perform that task.

Dynamic content - objects identifiers, variables, business rules
In all prompts, it's possible to use any object identifiers, variable and business rules, this enhances a prompt from just static text to context specific instructions. In that regard, it's similar to a SQL query editor, but does not demand using a proper SQL query syntax, instead instructions are written in plain text.
Prompts are always interpreted in a context of a particular workflow instance and all variables will be substituted with appropriate content.
Using object identifiers helps AI Agent to use specific path or put a result in a specific form field.
Using variables allows to insert values from the form fields inside a prompt to make it specific for each processed instance of a workflow.
An example has been already presented above, in the case of generating content on the given subject an in a specific style.
Business rules allows to insert values from any place of the system - including data sources.
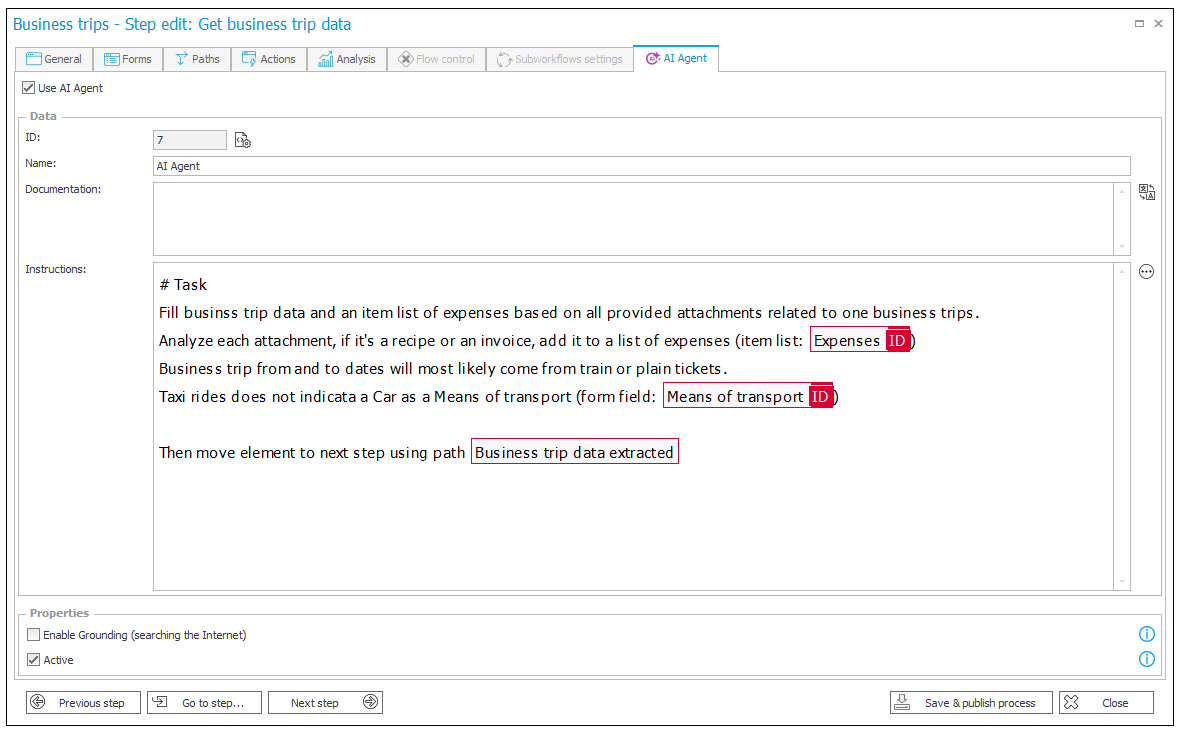
As an example, consider a process for storing meeting notes and preparation for next meetings. This can be a part of a larger CRM application.
First workflow will be responsible for meetings transcription, summarization and responding to Client. Transcription is created using AI Create transcription action. Internal summary and the response is prepared by AI Agents.
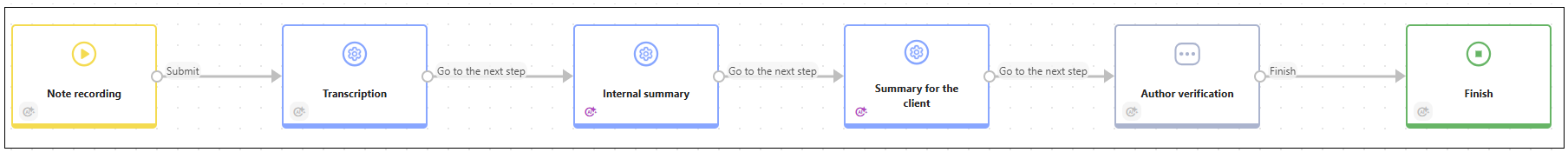
Second workflow support users in preparation for next meetings.
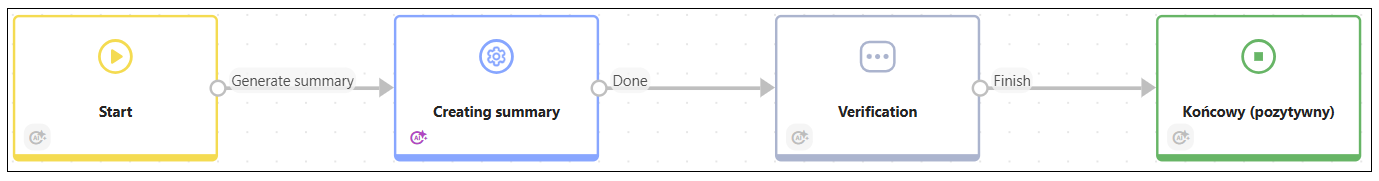
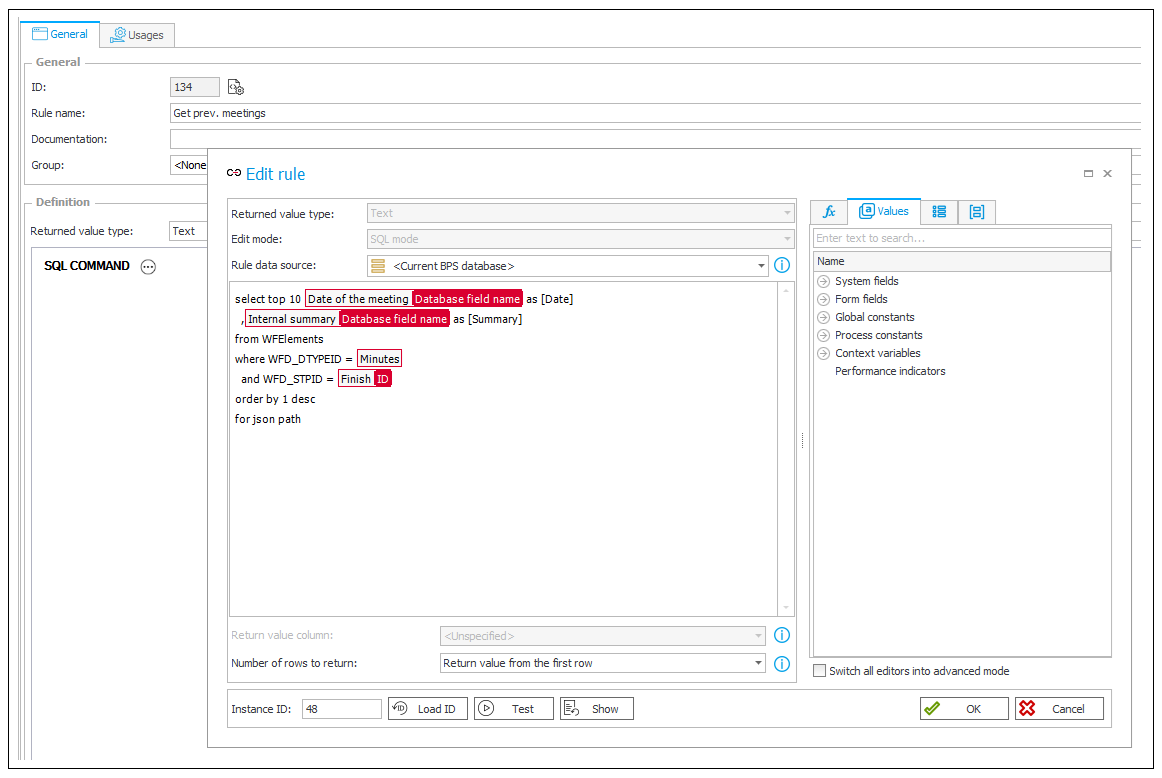
In this workflow, AI Agent receives summaries of previous notes as part of the instruction though a business rule.
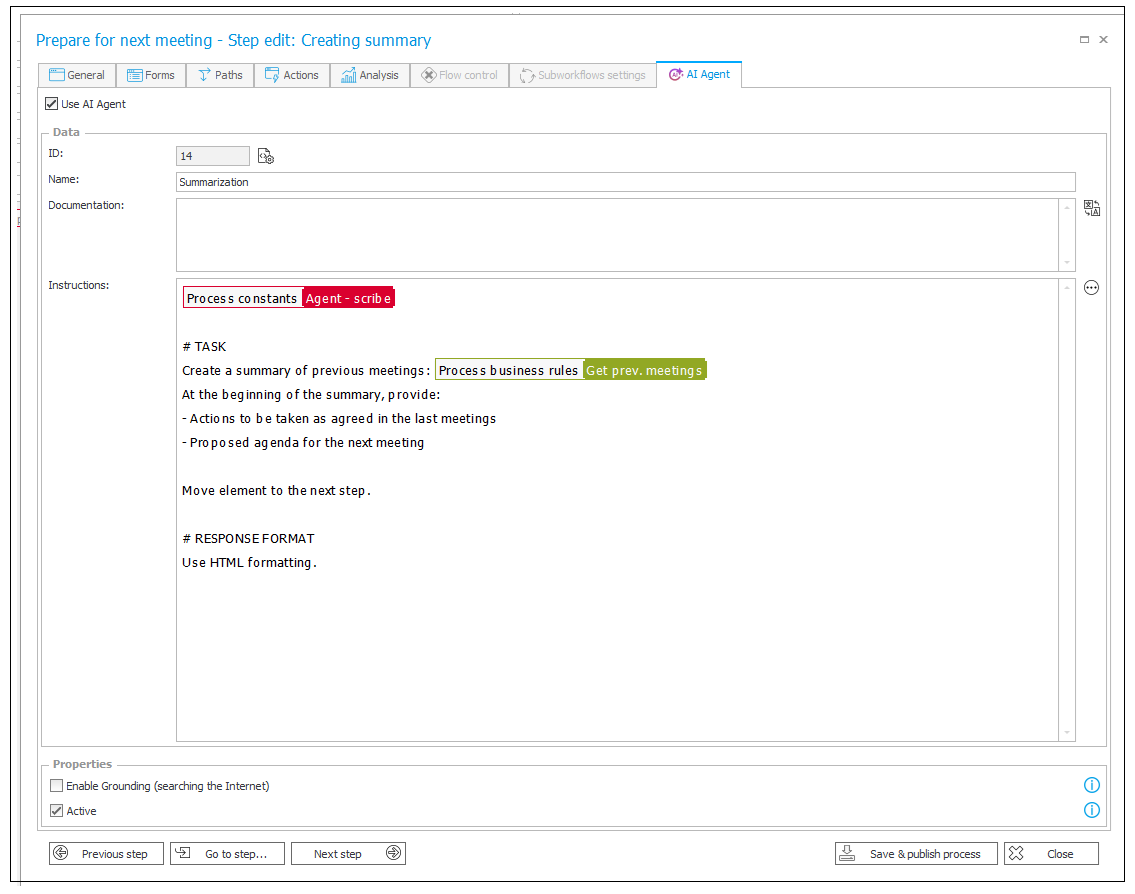
Business rule is define as follows
After generating a summary, this is how a form on "Verification" step can look like:

Reuse instructions
Shared instructions - such as role description or response formats - can be saved in one place to be reused across the system.
Constants
First option is to use process or global constants.
// process / global constant
Name: `AI Expert - Marketing Content Creator (description)`
Value: `You are a creative content creator specializing in marketing materials designed for use across various communication channels.
You are familiar with the latest trends in the low-code platform market, and the content you create relates to topics such as business process automation, low-code, RPA, etc.`.
Then use this constant in all places relevant to that AI Expert.

Dictionary processes
Second option is to use Dictionary processes. Combining them with global constants (storing each AI Experts ID) and a business rule to retrieve a description of a given AI Expert results in reusable configuration and easy modifications by the end users.


Structured output
When working with text outputs it is sometimes useful to specify the response format. In the most basic case, when text itself is the final result, it means guiding AI to use some specific order of content, using bullet points, markdown, html, headers etc.
// AI Agent or AI PROMPT
# TASK
Based on the attached file containing a description of the client meeting, create a short summary note of the meeting. The note is for internal use only.
# RESPONSE FORMAT
Internal Summary:
- Topics discussed
- Decisions made
- Tasks to be completed (with assignment and deadline)
- Final conclusions
Communication style:
- Concise, technical, operational
More advanced use case is to ask AI to return a structured response to be then processed with subsequent business rules or actions.
Collections
This leverages the concept of collections, which in WEBCON BPS business rules are a lists of values separated by ;. This allows easy parsing using GET AT INDEX [] [] business rule or FOR EACH operator.
// AI PROMPT
# TASK
Rate something from 1 - 5 and provide a short justification.
# RESPONSE FORMAT
Respond in the format: "{Rating};{Justification}", where:
{Rating}: a number from 0 to 5, with 5 being the highest rating.
{Justification}: a brief justification for the rating, with a maximum of 255 characters.
Response from AI PROMPT can be saved as local automation parameter or technical form field and later extracted by business rules:
GET AT INDEX [1] [{response}] = {Rating}GET AT INDEX [2] [{response}] = {Justification}
JSON
Return a JSON object can be useful to process the result using SQL or JavaScript. It can be achieved by simply explaining a desired output JSON structure or using json-schema.
// AI PROMPT
# ROLE
You assist users in filling out purchase requests.
# TASK
Analyze the user's description. If it's a purchase or demand, return:
# RESPONSE FORMAT
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema#",
"type": "object",
"description": "Purchase request assistant response",
"properties": {
"Category": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Request category: Software, Hardware, or Services"
},
"ShortTitle": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Brief summary of the request"
},
"AverageCost": {
"type": "number",
"description": "Estimated cost of the item or service"
},
"Hint": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Suggestion for improving the request description"
}
},
"required": ["Category", "ShortTitle", "AverageCost", "Hint"]
}
Result can be process by a form rule in JS mode:
AIresponse = JSON.parse(GetValue('#{FLD:1}#'));
SetValue('#{FLD:2}#', AIresponse.ShortTitle);
SetTypedValue('#{FLD:3}#', { value: AIresponse.AverageCost });
SetValue('#{FLD:4}#', AIresponse.Category);
if (AIresponse.Hint !== undefined) {
SetValue('#{FLD:5}#', AIresponse.Hint);
ShowField('#{FLD:6}#');
}
// replace #{FLD:X}# with form fields identifiers
See this article on WEBCON community for use cases implementing that approach.
Internal tools
All AI Agent and AI Concierge functionalities are built around internal tools, each designed for a specific job. Tools allow AI to interact with WEBCON BPS workflows and forms.
Although it is not possible to modify these tools from Designer Studio, understanding how they work may help writing better instructions for AI Agents and AI Concierge.
AI PROMPT is completely independent from these tools - the result is solely dependent on the provided instructions.
ToolChooser
Entry point for each request to AI Agent and AI Concierge. It's job is to understand the user's request and select best tools to achieve requested result. For AI Agents, it also decides whether or not to add attachments to the context of each tool. Attachments are selected by their name and their content will be analyzed in the subsequent tools.
ToolChooser should be able to select the best tools by itself, but,
in order to guide it towards specific tools, use specific Keywords associated with the tool (listed below for each tool).
PathChooser
This tool is used to select a path. In AI Agent, it will determine which path will be used by an Agent. In AI Concierge, the selected path will be suggested to the user.
Keywords
- English:
Go to the next step,Continue to the next section,Proceed,Move forward,Advance to the next step - Polish:
Przejdź dalej,Przejdź do kolejnego kroku,Wybierz ścieżkę
FieldSetter
This tool is used to assign new form field values. It has variants, designed for setting simple fields (text, date, numbers), setting picker fields and updating item lists.
Keywords
- English:
Fill in the field,Enter the value,Complete this section,Type in - Polish:
UzupełnijWpisz,Wypełnij
PickerSetter
This tool is invoked for each picker to be set. It resolve values available in the datasource, according to the form field settings:
- only visible columns are included
- limits the number of rows to 100 (in accordance with standard business logic, larger datasources require filtering). Dropdowns are an exception - entire data source is going to be sent.
Before setting values, system will validate, if value suggested by AI is present in the list of available values. If value is not present, it will not be set, even if a target field is required. Rationale: it's better to not set incorrect values. For that reason, it may be beneficial to disable form field validations for path used by AI Agents.
SubElements (Item lists)
There are three tools used for working with Item lists for adding, deleting and modifying rows and cell.
When setting picker fields on item lists, datasource values are calculated for a default row (like if a user would click "Add").
Keywords
- English:
Add a new line,Add an item,Insert a row,Update the line,Change the item,Modify row 3 - Polish:
Dodaj nową pozycję,Dodaj wiersz,Zaktualizuj wiersz,Zmień pozycję
DescriptionGenerator – for generating or requesting descriptions
This is a tool for AI Concierge, used whenever user asks for descriptions or summarization of what is currently visible in the Portal.
Keywords
- English:
Describe what you see,What is shown in the image?,Summarize the contentExplain what’s happeningWhat can be observed? - Polish:
Opisz,Co widać,Podsumuj,Podaj
Debugging
AI Agent
List of all AI Agent Jobs to be executed and completed can be found in Designer Studio > Reports > Basic reports > AI Agent Jobs. This report presents data from last 14 days, and is by default sorted by latest date of completion (if JOB is already processed) or insertion.
Successfully completed AI Jobs will have a reasoning provided, which gives insight in to which tools and why were selected by AI.
Example reasoning, return by AI Agent:
// AI Agent
# TASK
Briefly review whether the provided content aligns with the topic "New UI" and the style "Landing page description". Check spelling, grammar, and style.
# RESPONSE FORMAT
Respond only in plain text, without HTML, markdown, or icons. You may use new lines and bullet points using the '-' character.
// Reasoning
[
{
"Reasoning": "The user`s message requires reviewing content for alignment with a topic and style, checking spelling, grammar, and style, which involves setting form fields. The FormFieldSetter tool is selected to fill the required `Review` field. The PathChooser tool is selected to determine the appropriate path for moving the instance to the next step. No attachments are selected because the user`s message does not mention any attachments. No pickers are selected because there are no specific instructions on setting any pickers based on the context and available tools. The ElementSaver is not selected because user asks to navigate to another step.",
"Operation": "CreateSession"
},
{
"Reasoning": "The `Review` field was updated based on the analysis of the provided content in relation to the `Landing page description` style. The analysis highlights areas for improvement regarding style, grammar, and content focus.",
"Operation": "FormFieldSetter"
},
{
"Reasoning": "The user`s task is to review the content and fill the form fields, so the path `finish review` is the most appropriate to submit the instance to the next step after the review.",
"Operation": "PathChooser"
}
]
AI Concierge
Reasoning, similar to the examples for AI Agents, can be found in diagnostic mode.
Advanced AI PROMPT
Tool selection
Some decisions can't be made by deterministic IF/THEN algorithm, but once the decision is made, it's clear what to do next. In such cases, AI PROMPT can implement this decision logic and the rest of the execution can be handled by other actions available in WEBCON BPS.
By requesting AI to return a specific keyword, associated with one of next available actions it's easy to create an effective SWITCH statement (or use it in flow control step) to execute an action selected by AI. Result of that action can itself be passed to AI PROMPT or saved on the form and used by AI Agent.
# Task
You'll be given a simple math problem select the best tool to solve it.
# Tools:
## `Add`
Adds two integers.
Parameters: `a`, `b` two numbers to be added
## `Multiply`
Multiplies two integers.
Parameters: `a`, `b` two numbers to be multiplied
# Output
Always return values in this format: `tool_name`;`a`;`b`
Automation:

AI PROMPT:

Usage:
